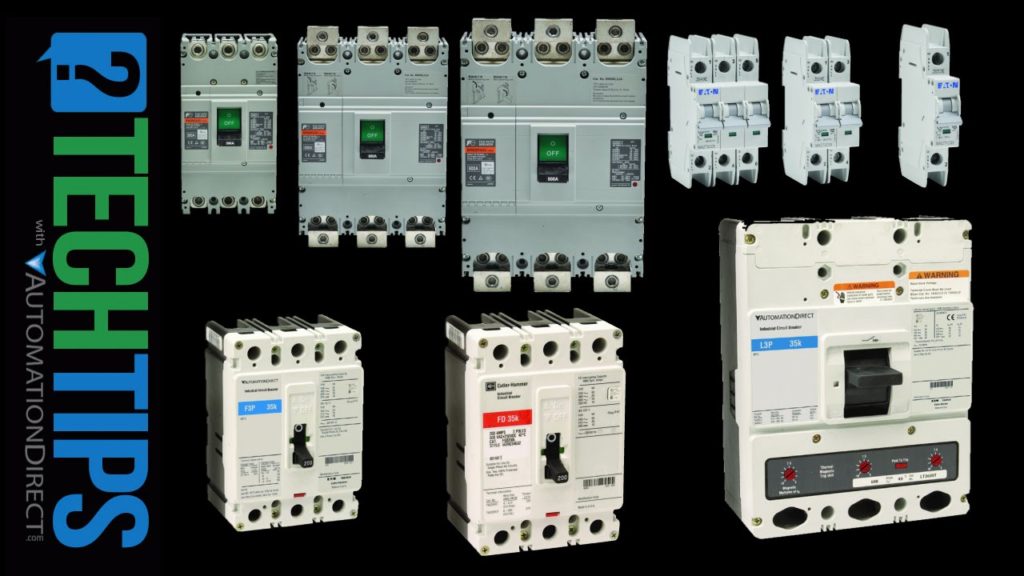
Your Trustful Circuit Breaker Supplier
Discover the power of advanced technology with Industrial Automation Products from Yingwangxin. As a leading automation products company, our product range includes drives, PLC modules, inverters, HMI’s, motors, control systems, power supply, circuit breaker and more, all designed to enhance operational efficiency. With products from leading brands like Siemens, Mitsubishi, Allen-Bradley,ABB and etc, we offer solutions that are reliable, high-quality, and tailored to your specific needs.
Showing all 12 results
-
Circuit Breaker
LV432876 Schneider Molded Case Circuit Breaker Expedited Shipping LV432876 GQ
Read moreRated 0 out of 5 -
Circuit Breaker
New 1Pcs GV2ME10C Telemecanique Circuit Breaker Schneider GV2-ME10C Plc Module
Read moreRated 0 out of 5 -
Circuit Breaker
New Schneider Electric LV429407 Circuit Breaker Under Voltage Release Module
Read moreRated 0 out of 5 -
Circuit Breaker
Schneider 1PCS Brand New LV431630 Molded Case Circuit Breaker Fast Ship
Read moreRated 0 out of 5
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
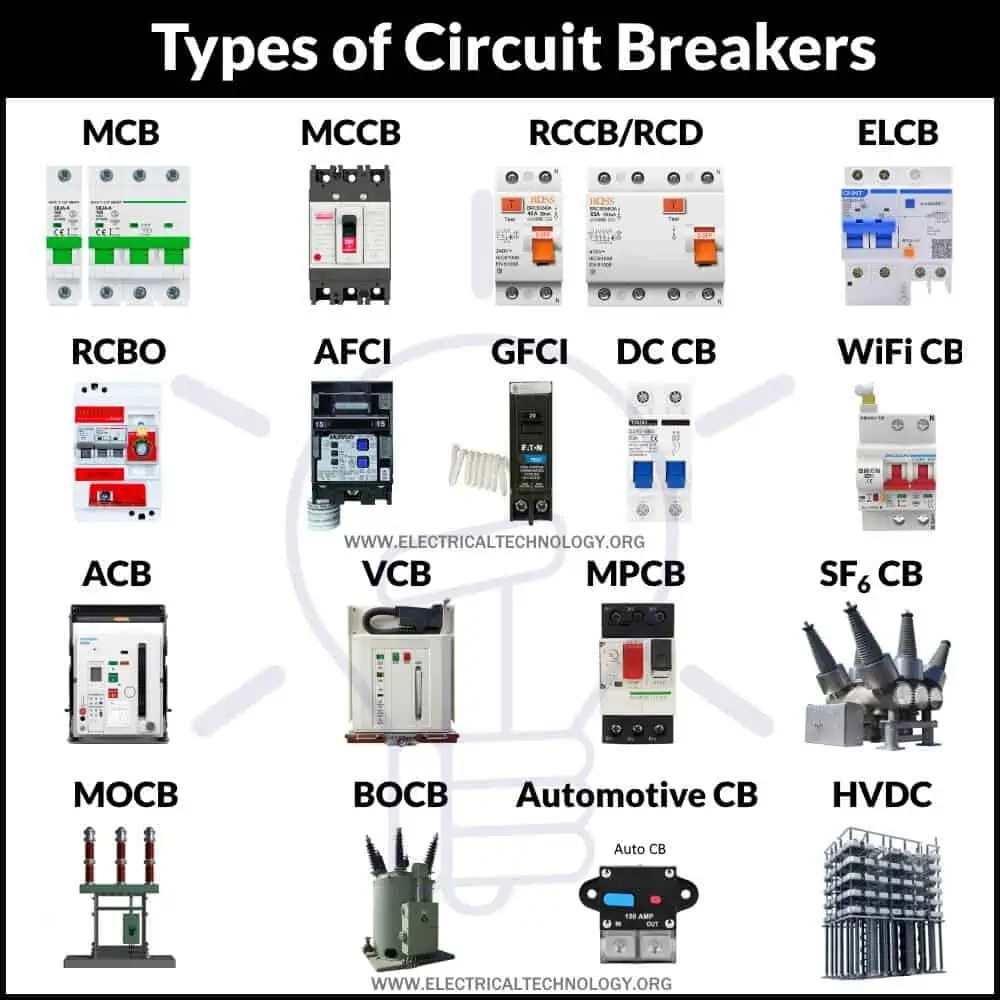
All You Need to Know About Industrial Circuit Breaker

Features of Industrial Circuit Breaker
High Rated Current
Can handle significantly higher current levels compared to standard household circuit breakers, suitable for large industrial loads.
Adjustable Trip Settings
Allows customization of overload and short circuit protection levels based on specific application needs.
Arc Extinguishing Mechanism
Effective design to quickly extinguish electrical arcs generated when interrupting a fault, preventing damage and fire hazards.
Robust Construction
Durable design to withstand harsh industrial environments and heavy duty operations.
Multiple Pole Configurations
Available in various pole arrangements (single, two, three) to match the electrical system.
Voltage Rating
Designed for high voltage applications depending on the industrial setting.
Operating Mechanism
Reliable mechanism to quickly open and close the circuit breaker under fault conditions.
Monitoring Capabilities
Some industrial breakers include features for monitoring current, temperature, and other parameters to detect potential issues.
Environmental Compatibility
Can be designed to operate in various environments, including outdoor installations.
Standards Compliance
Adheres to relevant electrical safety standards for industrial applications.
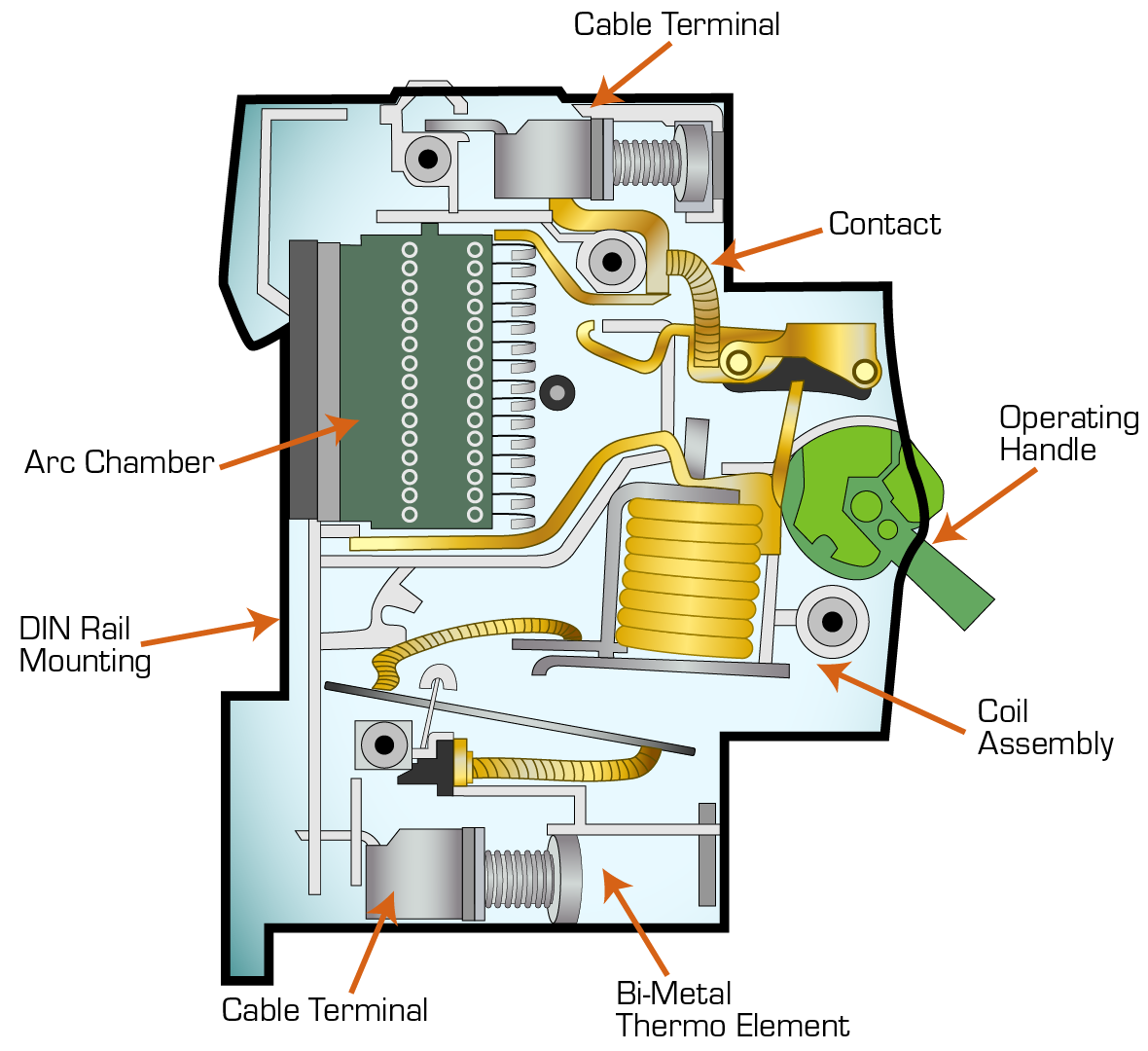
How Does the Industrial Circuit Breaker work?
An industrial circuit breaker functions by automatically interrupting the electrical current flow when it detects an overload or short circuit in a circuit, essentially acting as a safety device that protects equipment and prevents damage by breaking the connection when excessive current is present; it does this through a combination of thermal and magnetic mechanisms, where a bimetallic strip heats up due to high current, causing it to bend and trigger the tripping mechanism, while an electromagnet also activates under high current surges to rapidly open the circuit contacts; unlike fuses, circuit breakers can be reset and reused after tripping.
What Are Applications of Industrial Circuit Breaker?
- Manufacturing plants:Industrial circuit breakers are used to protect electrical machines, such as transformers, capacitors, and generators, from fire or explosion hazards.
- Power plants:Industrial circuit breakers protect generators, transformers, and electrical systems from overloads, short circuits, and costly downtime.
- Data centers:Industrial circuit breakers are used to ensure uninterrupted power.
- Renewable energy sector:Industrial circuit breakers are used to maintain the security and reliability of electrical systems in wind and solar farms.
- Chemical processing facilities:Industrial circuit breakers are used to protect complex electrical systems.

Different type of Industrial Circuit Breaker
There are four main ways to classify breakers in industrial applications:
- Voltage – Can be low-, medium-, or high-voltage
- Location – Only certain breakers are rated for outdoor use
- Interrupting mechanism – There are many systems for stopping current flow and power, including MCCB, vacuum, air, oil, & ICCB
- External design – Can be dead tank (has an enclosure at ground potential, housing interrupting & insulating mediums) or live tank (housing interrupters are at potential above ground, with insulation in between)
9 Steps Toward the Best Industrial Circuit Breaker Type
The top criteria for selecting an industrial-grade circuit breaker are:
#1 Voltage Rating
Matching your breaker to your application’s needs is probably your first order of business.
The rated voltage of a circuit breaker refers to the number of volts it can handle safely. A mismatch between the breaker’s rating and your system’s voltage levels can lead to inefficiency and may compromise safety.
#2 Current Rating
Rated current is the maximum current that a circuit breaker can carry continuously in the ambient temperature where it was calibrated.
Continuous current rating should align with the requirements of your system.
A too-high current rating may keep the breaker from tripping when it’s supposed to. This allows excessive current to flow through the circuit, potentially leading to overheating, equipment damage, and even a visit from the fire department.
A too-low current rating will cause the device to trip too easily, even under normal operating conditions. This can result in frequent production stoppages, with the breaker becoming the very thing it was meant to prevent – downtime.
#3
Interrupting Capacity
A breaker’s interrupting capacity must be equal to or greater than the potential fault current your system may produce where the breaker is applied.
The number of appliances and electronics requiring a higher interrupting capacity is on the rise. With many facilities running multiple large appliances simultaneously, it’s become easy to trip the old standby of 10,000 A capacity. Larger operations will value this spec more than others because it’ll allow them to function safely and avoid tripping the breaker repeatedly.
#4
Frequency
The frequency rating of a circuit breaker should match the frequency of your electrical system. (Sound like familiar advice?)
Mismatches can lead to operational inefficiencies and may even damage the circuit breaker or the system it protects. For example, using a circuit breaker rated for 50 Hz in a 60 Hz system could reduce the system’s power rating and shorten the breaker’s life span.
Circuit breakers up to 600 A can be applied to frequencies of 50-120 Hz. Assemblies with frequencies of more than 120 Hz frequencies will force you to derate the breaker.
#5
Tripping Current Level Adjustment Ranges
Modern circuit breakers often come with adjustable tripping current levels for both overload and short-circuit protection. This feature allows you to better tailor the circuit breaker’s performance to your needs.
#6
Environmental Resistance
Environmental threats are of special concern if you’re in an industry like oil and gas, food, or mining. If your project includes a unique or extreme environment, look for circuit breakers that have relevant certifications.
#7
Number of Poles
Breakers come in single-pole construction or multi-unit assemblies. Single-pole breakers are common in homes, but industrial applications often require multi-pole breakers for three-phase systems.
In the end, the choice between single and multi-pole will depend on the complexity of your electrical system. Consider also whether you’ll need to isolate individual phases for maintenance or troubleshooting.
#8
Testing/Maintenance
Note that manually operated breakers require less maintenance. They need only a simple cleaning of their contacts and verification that their linkages operate freely. Consider the ease and cost of maintaining the circuit breaker when making your choice.
#9
Setup
Physical dimensions and setup matter beyond just the current rating of the circuit breaker.
Breaker size is an oft-forgotten consideration for settings where space is at a premium. Make sure your industrial breaker fits your panel or distribution board while still meeting other electrical requirements.
When it comes time to install the breaker, there are several more steps, including mounting, wiring, and testing. Consider the complexity of the setup process and whether you’ll need specialized tools or expertise for a successful installation.
There are more circuit breaker mounting types than you could imagine. You can mount most breakers in any position, vertically or horizontally, without affecting their function.
In windy areas, the breaker should include an enclosure and be mountable on a surface that’s not overly rigid. A breaker attached to a stiff assembly may not perform as well in high winds.
Request A Free Quote
We'd like to work with you
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. Our experts will give you a reply within 24 hours and help you select the right valve you want.
- +86 175 0301 5773
- +86 189 2656 9286
- info@yingwangxin.com